Sliding Window Patterns
Sliding Window Patterns
Sliding window Technique(SWT) is basically finding subarrays of an array given the that they satisfy a particular condition. Now, majority of SWT problems are on arrays and strings, both itrable objects, the idea is to iterate through the given object using a sliding sub-array of either given length of variable length. This technique comes under Dynamic Programming since we solve this by maintaining a subset of items as our window and resizing and moving that window within the larger array/string until we find a solution.
There are two type of Sliding Window Problems -
- Window size is fixed and sub-array satisfy some condition.
- Window size is unknown and we need to find sub-array which satisfies some condition.
Problem Statement
Let us look at a sample problem which comes under SWT Type I.
Given an array, find the average of all subarrays of ‘K’ contiguous elements in it.

Let’s take K = 3 then the idea is SWT visually is,
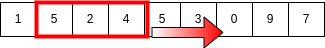
Brute Force
The simple brute force approach for the given problem is:
- Calculate all possible subarrays with k elements using two for loops.
- The inner for loop goes over k contigous arrays.
- Time complexity: O(N*K):
- Space complexity: O(N) for creating extra list.
Code for Brute Force Approach
def average_of_k_subarray(k, arr):
result = []
for i in range(len(arr)-k+1):
total = 0
for j in range(i, i+k):
total += arr[j]
result.append(total/k)
return result
In case of brute force one thing to notice here is that when we are sliding over the array we are repeatedly calculating sum of k elements all over. We can definitely optimize that. Let us see how.
Sliding Window
Finally we come down to the actual algorithm. As we discussed we make use of previously summed elements,
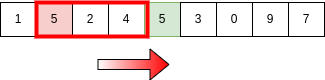
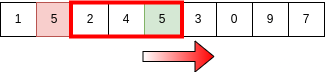
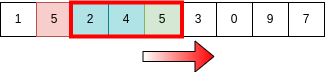
General Algorithm for SWT is -
- Iterate over the array
- Slide the window forward and calculate the sum of the new position of the sliding window.
- Subtract the element going out of the sliding window, i.e., subtract the first element of the window.
- Add the new element getting included in the sliding window, i.e., the element coming right after the end of the window.
PYTHON CODE FOR SLINDING WINDOW ALGORITHM
def average_of_k_subarray(arr):
averages = []
wSum = 0
wStart = 0
for wEnd in range(len(arr)):
wSum += arr[wEnd]
if wEnd>=k-1:
averages.append(wSum/k)
wSum -= arr[wStart]
wStart += 1
return averages
Now, we will look at a couple of problems, of both the types.
Problem I
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘k,’ find the maximum sum of any contiguous subarray of size ‘k’.
Input: [2, 1, 7, 1, 4, 2], k=3
Output: 12
Subarray with maximum sum is [7, 1, 4].
Brute Force Approach Let us look at brute force approach
def max_sum_subarray(k, arr):
mSum = 0
wSum = 0
for i in range(len(arr)):
for j in range(i-k+1):
wSum += arr[j]
mSum = max(mSum, wSum)
return mSum
Time Complexity is O(N*K) Space Complexity is O(1)
Sliding Window Technique
def max_sum_subarray(k, arr):
wSum = 0
mSum = 0
mStart = 0
for mEnd in range(len(arr)):
wSum += arr[wEnd]
if wEnd >= k-1:
mSum = max(wSum, mSum)
wSum -= arr[wStart]
wStart +=1
return mSum
Time Complexity is O(N) Space Complexity is O(1)
Problem II
Given an array of positive numbers and a positive number ‘S’ find the length of the smallest contiguous subarray whose sum is greater than or equal to ‘S’. Return 0 if no such subarray exists.
Input: [2, 1, 6, 3, 3, 2], S=9
Output: 2
Explanation: The smallest subarray with a sum greater than or equal to ‘9’ is [6, 3].
The strategy used to solve this problem is simmi;lar to the previous problem, the difference is the variable window size. Approach to solve this problem
- Start with adding up the elements from the beginning of the array until their sum becomes greater than or equal to ‘S’
- These elements will become the sliding window. We are asked to find the smallest such window having a sum greater than or equal to ‘S.’ We will remember the length of this window as the smallest window so far.
- After this, we will keep adding one element in the sliding window (i.e., slide the window ahead) in a stepwise fashion.
- In each step, we will also try to shrink the window from the beginning. We will shrink the window until the window’s sum is smaller than ‘S’ again. This is needed as we intend to find the smallest window. This shrinking will also happen in multiple steps; in each step, we will do two things: i.Check if the current window length is the smallest so far, and if so, remember its length. ii. Subtract the first element of the window from the running sum to shrink the sliding window.
Sliding Window Technique
def max_sum_subarray(s, arr):
wSum = 0
minLen = float('inf')
wStart = 0
for mEnd in range(len(arr)):
wSum += arr[wEnd]
while wEnd >= s:
minLen = min(minLen, wEnd-wStart+1)
wSum -= arr[wStart]
wStart +=1
if minLen == float('inf'):
return 0
return minLen
Time Complexity for this solution is O(N) since there is only pass over the array and Space Complexity is O(1).
Conclusion
You will notice that once in the optimized algorithm, there are certain steps which will be common to any problem. What is important for this algorithm or any other algorithm is to understand the patterns occuring in the logic. More problems on sliding window can be found here
Hope you all are able take away something from here. Please share the post and subscribe to the blog. If you find any mistake in what I have written or error in the code please drop a mail, I will do the needful as required. Until next time!


Leave a comment